How to determine your Design’s Success?
Design validation is the process of ensuring that a design meets the needs of its intended users and that it functions as intended. This is a crucial step in the design process, as it ensures that the design will be successful in the real world. However, knowing whether your design is good can be challenging, and there are several factors to consider.
Why is Design Validation Important?
Design validation is essential because it helps to identify any issues or shortcomings in a design before it is released to the market. This means that any problems can be addressed early on, reducing the likelihood of costly recalls or redesigns. By validating the design, you can also gain valuable insights into user behavior and preferences, which can inform future design decisions.
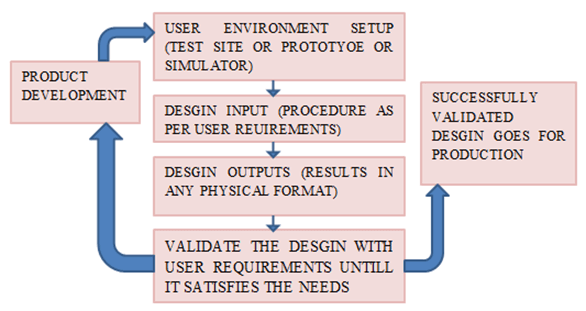
Validation Techniques
There are several techniques used in the industry for validating the design. Some of the most common techniques include:
Usability Testing
Usability testing is a popular technique for design validation, as it provides direct feedback from real users.
Usability testing typically involves the following steps:
- Planning: Define the objectives of the usability test and identify the target audience. Develop a test plan, including a script and a list of tasks for the users to perform.
- Recruiting: Recruit a group of users who fit the target audience. Users can be recruited from a variety of sources, such as online communities, social media, or through a research panel.
- Conducting the Test: Conduct the test in a controlled environment, such as a usability lab or a remote testing platform.
- Analyzing the Results: Analyze the results of the usability test and identify any issues with the design.
- Iterating: Make changes to the design based on the feedback from the usability test. Conduct additional testing to ensure that the changes have addressed the issues identified in the first test.
By using usability testing to validate a design, designers can gain valuable insights into how users interact with the product and identify any issues with the design.
Hallway Testing and Peer Review
Hallway testing is a quick and informal way to gather feedback on a design. It involves showing the design to people in a public space, such as a hallway or a coffee shop, and asking for feedback. This feedback can be used to identify any issues with the design and make improvements.
For instance, an e-commerce website might do hallway testing by asking random visitors to their site to try to complete a purchase and provide feedback on any issues or confusion they encountered.
Peer review is another technique that can be used to validate a design. Peer review involves having a team of experts review the design and provide feedback. This can include designers, engineers, and other professionals who can provide valuable insights into the design.
For example, a graphic designer might ask other designers to review a new logo design and provide feedback on its visual appeal, branding, and legibility.
Nielsen’s 10 heuristic
Design validation can also be done through the use of Nielsen’s 10 heuristics, which are a set of guidelines for user interface design. These heuristics were developed by Jakob Nielsen, a renowned user experience (UX) expert, and have been widely adopted as a standard for evaluating the quality of user interfaces.
The 10 heuristics are as follows:
- Visibility of system status
- Match between the system and the natural world
- User control and freedom
- Consistency and standards
- Error prevention
- Recognition rather than recall
- Flexibility and efficiency of use
- Aesthetic and minimalist design
- Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors
- Help and documentation
Analytics and benchmarking
Design validation can also be done through the use of analytics and benchmarking. Analytics involves gathering data on how users interact with a product, such as how long they spend on a particular page or which features they use the most. This data can be used to identify any issues with the design and make improvements. Benchmarking involves comparing a product to similar products on the market to identify strengths and weaknesses. This can be done by gathering data on how users interact with competitor products and comparing it to the data gathered from your product.

A/B Testing
Design validation can also be done through A/B testing. A/B testing involves comparing two versions of a design, A and B, to see which one performs better. This can be done by randomly showing users either version A or version B and collecting data on their interactions with the design. A/B testing is particularly useful for validating changes to the design, such as changes to the layout or content of a page. By testing different versions of the design, designers can identify which changes are effective and make informed decisions about how to improve the design.
An example of A/B Testing would be Call-to-Action (CTA) Copy. An e-commerce website could test two different versions of a call-to-action button, such as “Buy Now” versus “Add to Cart” to see which one generates more conversions.
Another Example would be:
“Get Started with Our Free Trial Today!”
This CTA copy uses the action verb “Get Started” to communicate the desired action of signing up for the free trial. The use of urgency with the word “Today” adds a sense of immediacy, and the use of first-person language with the word “Our” makes the call to action feel more personal. Finally, the benefit of trying the product for free is highlighted, which could increase the user’s motivation to take action.
Expert Review
Design validation can also be done through expert review. An expert review involves having a team of experienced designers and /or usability experts evaluate a design and provide feedback. This feedback can be used to identify any issues with the design and make improvements. An expert review is a quick and relatively inexpensive way to gather feedback on a design. It can be instrumental in the early stages of the design process, when a design may not yet be ready for usability testing. By using expert review to evaluate a design, designers can benefit from the expertise of experienced professionals and ensure that their design meets established design standards.
Stakeholder Interviews
Design validation can also be done through stakeholder interviews. Stakeholder interviews involve talking to key stakeholders, such as business owners, product managers, or customer service representatives, to gather feedback on a design. This feedback can be used to identify any issues with the design and make improvements.
By using stakeholder interviews to evaluate a design, designers can gather valuable feedback on the business objectives and user needs that the design should be addressed. Stakeholder interviews can also help identify any potential roadblocks to the success of the design, such as technical limitations or budget constraints.
Conclusion
Design validation is a crucial step in the design process, and it is essential to ensure that a design meets the needs of its intended users and functions as intended. At f1studioz we ensure accessible and usable designs for all stakeholders. Design Validation is a crucial step in our design process through which we determine and ensure that the design meets all the user’s needs and business goals, as demonstrated here.
By considering key metrics such as user needs, functionality, performance, usability, and aesthetics, and using validation techniques such as user testing, A/B testing, expert review, analytics, and surveys, you can determine whether your design is good and is meeting all the goals for users as well as the businesses.







