As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to transform industries, the role of user experience (UX) design in developing AI-powered products becomes even more essential. At the heart of this intersection is the challenge of creating intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that ensure privacy and security.
For UX designers, especially those focused on AI, the task is not just about integrating AI into interfaces but designing experiences that make AI accessible, trustworthy, and secure for users.
Understanding the Role of UX in AI-Powered Experiences
AI can only process vast amounts of data and automate tasks; how the user views and interacts with these capabilities is determined by the UX design. The success of AI applications relies on creating user-friendly experiences, simplifying complex processes, and maintaining trust through transparent data handling.

For example, AI-driven features like personalised recommendations, automated customer support, and predictive analytics are only as good as the UX that delivers them. A well-designed interface can demystify AI for users, allowing them to understand and control how AI impacts their experience. This is particularly important in fostering user trust, as a clear and user-centric design can ease concerns about privacy and data security.
Challenges in UX Design for AI
1. Simplifying Complex AI Processes
One of the main challenges in UX design for AI is to make complex processes easy to understand and use for non-expert users. AI algorithms and models can be highly sophisticated, but if users cannot grasp their functionality or benefit from them, the AI’s potential is wasted.

Designers must focus on creating interfaces that abstract away the complexity of AI, presenting only essential information for users to accomplish their goals. Using visualizations and intuitive controls can help users interact with AI tools more effectively, making the technology more approachable.
A prime example would be Google’s AI-powered search engine. It uses simple, user-friendly interfaces to help users find information quickly, despite the complex algorithms working in the background.
2. Building Trust Through Transparency
AI systems often function as black boxes, making decisions based on complex algorithms that users find difficult to understand. This opacity can lead to mistrust, especially when personal data is involved.

According to a recent Pew Research Center survey, 81% of consumers believe that the information collected by AI companies will be used in ways people are uncomfortable with, as well as in ways that were not originally intended.
UX designers must work to make AI processes as transparent as possible, providing users with insights into how decisions are made and what data is being used.
3. Ensuring Privacy and Security
Privacy and security are paramount in AI-powered experiences, particularly when sensitive user data is involved. UX designers face the challenge of creating interfaces that protect user data while maintaining a smooth experience.

A KPMG study conducted in January 2024 found that 63% of consumers are concerned about the potential for generative AI to compromise an individual’s privacy by exposing personal data to breaches or other forms of unauthorised access or misuse.
Additionally, 86% of consumers care about data privacy, and 79% are willing to spend time and money to protect their data, according to Cisco’s “Building Consumer Confidence Through Transparency and Control” report.
Implementing strong security measures and communicating these measures effectively to users may help designers. Designers can incorporate privacy-first design principles, such as minimal data collection, transparent consent mechanisms, and easy-to-use privacy settings.
Opportunities in UX Design for AI
1. Prioritising User Control in AI-Powered Designs
Implementing user-centric design principles is essential for addressing privacy concerns and empowering users. UX designers should prioritise features that enable users to easily manage their data preferences, providing clear options for data sharing and privacy settings. This will also foster trust in AI systems.

To enhance user empowerment, designers can create interfaces that allow individuals to customise AI-driven recommendations and opt out of certain functionalities. By giving users greater control over their interactions with AI, designers ensure that the experiences are not only personalised but also respectful of user preferences and privacy.
Ultimately, this approach strengthens the relationship between users and AI, making technology feel more supportive and trustworthy.
2. Creating Ethical AI Interfaces
As AI becomes more prevalent, the ethical implications of its use come to the forefront. Companies that use AI ethically can be rewarded: According to a survey conducted by Capgemini, 62% of consumers said they would place higher trust in a company whose AI interactions they perceived as ethical.
Furthermore, 61% said they would share positive experiences with friends and family, and 59% said they would have higher loyalty to the company. By contrast, when consumers’ AI interactions result in ethical issues, 41% said they would complain, 36% would demand an explanation, and 34% would stop interacting with the company.
UX designers have a responsibility to consider how AI-driven interfaces impact users and society. This includes ensuring that AI systems do not perpetuate biases or unfair practices. For instance, designers can work to create AI interfaces that are inclusive and equitable, ensuring that all users have access to the benefits of AI.
The IEEE’s Ethical AI framework provides guidelines for developing AI systems that are transparent, accountable, and fair. UX designers can use these guidelines to create interfaces that reflect ethical AI principles, facilitating a positive impact on users and society at large.
3. Strong Security Features and Transparent Communication
Integrating strong security features into the design of AI-powered experiences is essential for protecting user data. Including implementing encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates can be beneficial. Educating users about these features can further enhance their confidence in the system.

Equally important is transparent communication regarding how user data is collected and used. UX designers can incorporate visual aids, such as infographics or tooltips, to explain complex AI processes in simple terms.
Displaying clear consent forms that outline data usage enhances user understanding and also builds trust in the system. By combining effective security measures with clear communication, designers can create a safer and more transparent environment for users interacting with AI technologies.
4. Enhancing AI’s Accessibility
AI’s potential can only be fully realized if it is accessible to all users, regardless of their technical expertise. UX designers can play a key role in making AI more accessible by creating interfaces that are intuitive and user-friendly.

This might involve designing AI tools that can be used with minimal training or creating interfaces that cater to users with varying levels of digital literacy.
Key Strategies for Designing AI-Powered User Experiences
Try following these strategies to successfully design UX for AI-powered experiences:
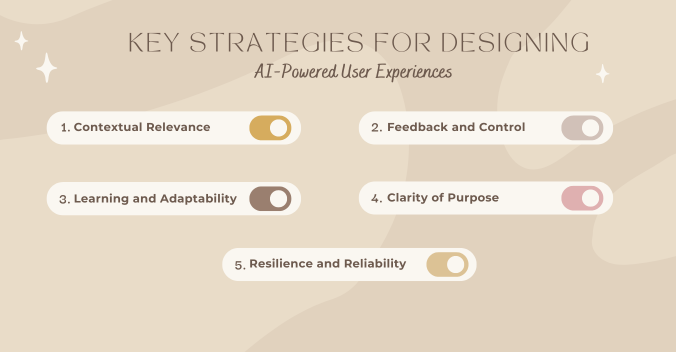
- Contextual Relevance: Design AI interactions that are context-aware, ensuring that the AI responses or actions are relevant to the user’s current environment or situation.
- Feedback and Control: Provide users with continuous feedback on how AI is operating and allow them to easily intervene or adjust AI behaviour if needed.
- Learning and Adaptability: Incorporate designs that allow the AI to learn from user interactions and adapt over time, improving its relevance and effectiveness based on user behavior and preferences.
- Clarity of Purpose: Ensure that the AI’s role in the user experience is clear from the outset. Users should easily understand what the AI is intended to do and how it benefits them, reducing confusion and increasing trust.
- Resilience and Reliability: Design AI-powered experiences that can gracefully handle errors or unexpected inputs. Ensuring that the system can recover from mistakes without negatively impacting the user experience is crucial for maintaining trust.
The Future of AI and UX Collaboration
Looking ahead, the role of UX in shaping AI-driven interactions will become even more critical as AI technologies advance. UX designers should anticipate how AI can be smoothly integrated into everyday experiences, ensuring that these interactions remain human-centered, intuitive, and secure.
One area that holds promise is the exploration of emotional intelligence in AI design. As AI systems become more advanced, there is an opportunity to create interactions that are not only functional but also emotionally meaningful.
By embedding empathy and emotional awareness into AI-driven interfaces, UX designers can create experiences that truly connect with users on a deeper level, enabling emotional engagement.
Also Read: Confused Users, Frustrated Results: Why AI Apps Need Great UX?